Day 7 Task: Understanding package manager and systemctl
Table of contents
- What is a package manager in Linux?
- What is a package?
- Different kinds of package managers
- You have to install docker and Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers.
- install docker
- Install Jenkins:
- check the status of the docker service in your system (make sure you completed the above tasks, else docker won't be installed)
- stop the service Jenkins and post before and after screenshots
- read about the commands systemctl vs service
What is a package manager in Linux?
A package manager is a software tool that allows users to install, remove, upgrade, configure and manage software packages on an operating system. It automates the installation process, upgrading process, configuration process, and removal process of the computer programs for an operating system of the computer efficiently. A package manager works with packages, data within archive files, and software distributions.
What is a package?
A package is usually referred to as an application but it could be a GUI application, command line tool or a software library (required by other software programs). A package is essentially an archive file containing the binary executable, configuration file and sometimes information about the dependencies.
Different kinds of package managers
Package Managers differ based on the packaging system but the same packaging system may have more than one package manager.
APT
(Advanced Package Tool) is a package manager used in Linux-based operating systems such as Debian, Ubuntu, and their derivatives? It is a command-line tool that simplifies the installation, removal, and updating of software packages in the system.
To update the package list from repositories. | Sudo apt update |
To upgrade all installed packages to the latest version | Sudo apt upgrade |
To install any package | Sudo apt install <package_name> |
To remove any package | Sudo apt remove <package_name> |
To search for a package that contains the keyword | Sudo apt search <keyword> |
To Show package information | Sudo apt show <package_name |
YUM:
(Yellowdog Updater, Modified) YUM is the default package manager for Red Hat-based distributions like CentOS and Fedora.
To update the package list from repositories. | Sudo yum update |
To upgrade any installed packages to the latest version | Sudo yum upgrade |
To install any package | Sudo yum install <package_name> |
To remove any package | Sudo yum remove <package_name> |
To search for a package that contains the keyword | Sudo yum search <keyword> |
To Show package information | Sudo yum info <package_name> |
Pacman :-
Pacman is the default package manager for Arch Linux and its derivatives. It is a command-line tool that allows you to search, install, update, and remove packages.
To update the package list from repositories. | Sudo pacman -syu |
To install any package | sudo pacman -S package_name |
To remove any package | sudo pacman -R package_name |
To search for a package that contains the keyword | sudo pacman -Ss keyword |
To Show package information | sudo pacman -Si package_name |
Zypper :-
Zypper is the default package manager for SUSE Linux and openSUSE distributions.
To update the package list from repositories. | sudo zypper refresh |
To upgrade any installed packages to the latest version | sudo zypper update |
To install any package | sudo zypper install package_name |
To remove any package | sudo zypper remove package_name |
To search for a package that contains the keyword | sudo zypper search keyword |
To Show package information | sudo zypper info package_name |
systemd is a system and service manager that is used to start, stop, and manage services and daemons in the background.
To start a service | sudo systemctl start <service_name> |
To stop any service | sudo systemctl stop <service_name> |
To restart any service | sudo systemctl restart <service_name> |
To enable a service to start automatically at boot time. | sudo systemctl enable <service_name> |
To disable service to start automatically at boot time. | sudo systemctl disable <service_name> |
To show the status of a service including whether it is running, stopped, or failed. | sudo systemctl status <service_name> |
To reload any service | sudo systemctl reload <service_name> |
To list all installed services in the system, along with their status and whether they are enabled or disabled. | systemctl list-unit-files --type=service |
To list all available services on the system and their status. | service --status-all |
You have to install docker and Jenkins in your system from your terminal using package managers.
install docker
sudo apt-get update #Update the package manager's cachesudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release #Install the necessary dependenciescurl -fsSLhttps://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg| sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg #Add the Docker GPG key to the systemecho "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg]https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null #Add the Docker repository to the systemsudo apt-get update #Update the package manager's cache againsudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-clicontainerd.io#Install Dockersudo docker run hello-world #Verify that Docker is installed correctly by running thehello-worldimage
cat /etc/apt/sources.list #To check docker downloaded files
cat /etc/apt/sources.list | grep -G "#" #To check files
\===============================================
Install Jenkins:
sudo apt-get update #Update the package manager's cache
sudo apt-get install -y openjdk-11-jdk #Install Java
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add - #Add the Jenkins repository key to the system
sudo sh -c 'echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list' #Add the Jenkins repository to the system
sudo apt-get update #Update the package manager's cache again
sudo apt-get install jenkins #Install Jenkins
sudo systemctl start jenkins #Start the Jenkins service
sudo systemctl status jenkins #Check the status of the Jenkins service
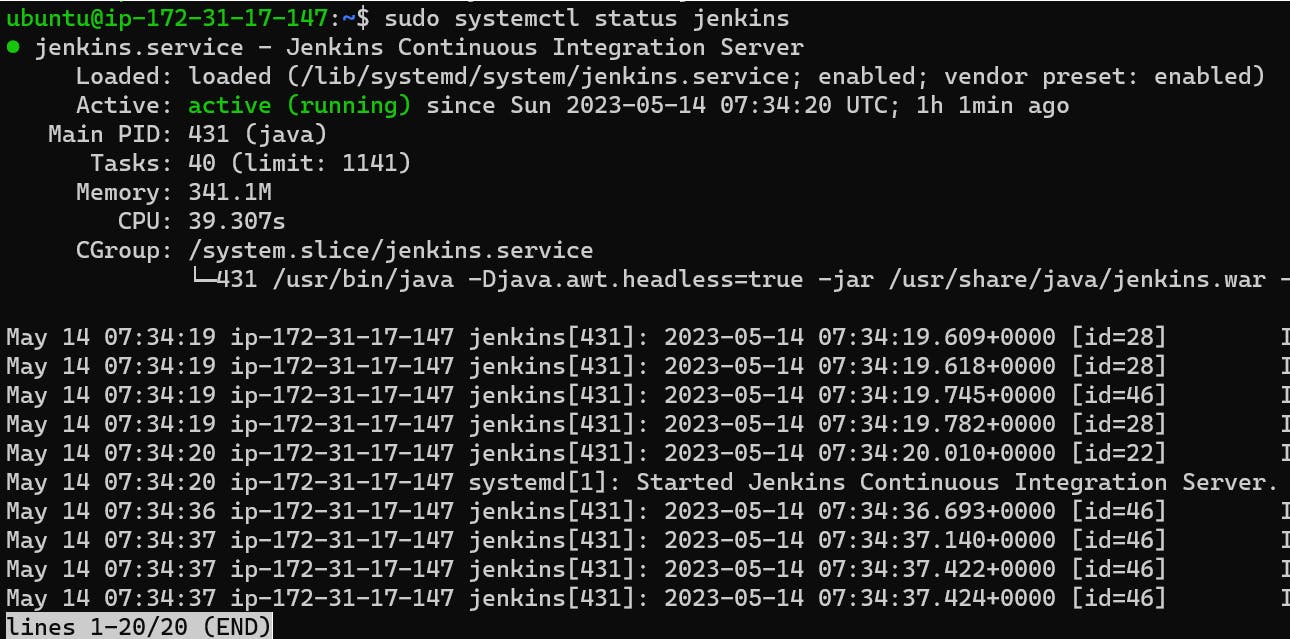
Open a web browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080 to access the Jenkins web interface.
\==========================================
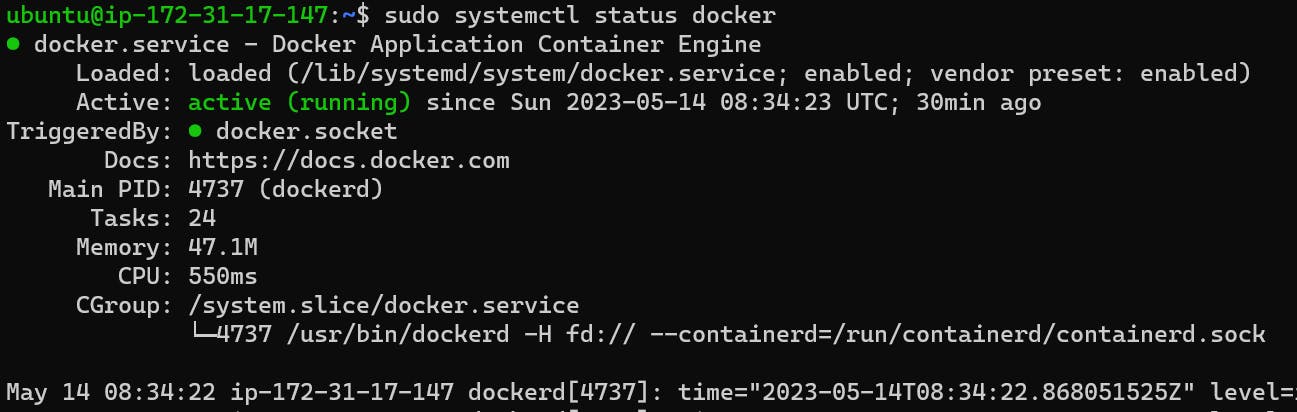
check the status of the docker service in your system (make sure you completed the above tasks, else docker won't be installed)
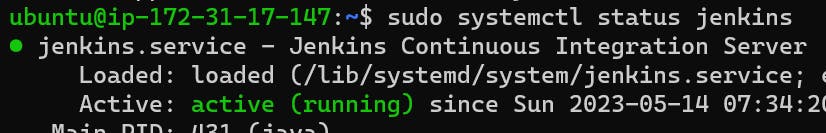
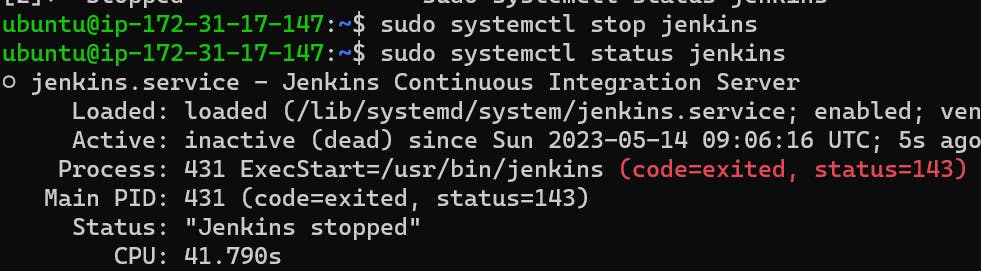
stop the service Jenkins and post before and after screenshots
read about the commands systemctl vs service
eg. systemctl status docker vs service docker status
systemctl status docker provides more detailed information and is the preferred command on modern Linux systems that use systemd. However, service docker status can still be used on older Linux systems that use init.d scripts.
\===========================================
Will appreciate your feedback :) #90daysofdevops
linkedin.com/in/sweety-samya-963859130
Happy learning!-